What is GSM?
GSM (Global System for Mobile communications) is a standard that describes the protocols for 2G cellular digital networks. 2G networks were developed as a replacement of 1G analog networks and then followed by 2.5G, 2.75G, 3G and 4G LTE.
The main difference between 1G and 2G is that 2G goes digital after the base station and is digitally encrypted. 2G is circuit switched network so it’s voice only. Data support came after 2.5G, which is also called GPRS (General Packet Radio Service). GPRS offers up to 50 Kbps theoretical transfer speed. (40 Kbps in practice)
GSM Network Architecture
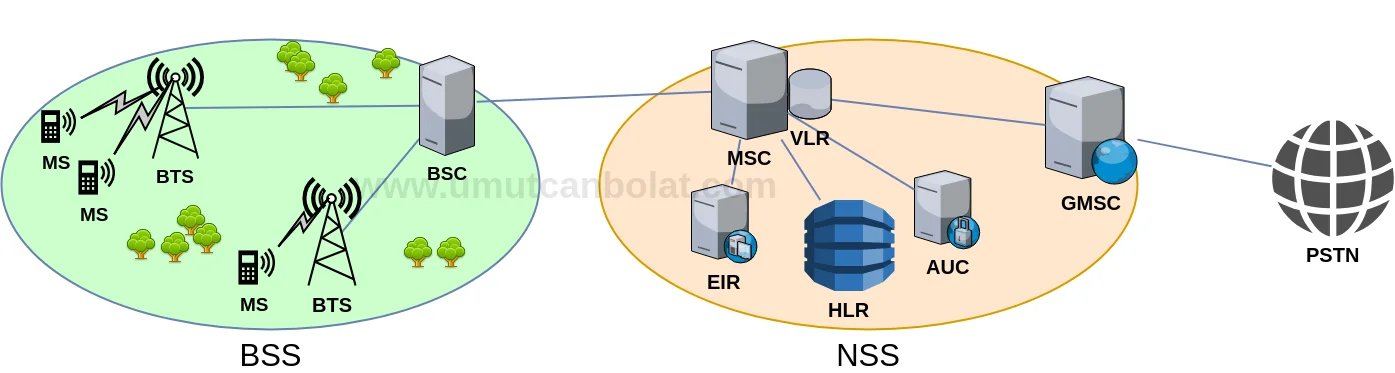
The overall GSM network can be seen above. It is divided into 2 parts. BSS (Base Station Subsystem) and NSS (Network Switching Subsystem). First we need to learn the meanings of the abbreviations before understanding the whole diagram. Let’s look at them one by one.
MS (Mobile Station)
MS is the user equipment such as cellphone, mobile computer or any other device which carries SIM card and have the software to communicate with the GSM network. In 3G systems, MS is referred to as UE (User Equipment).
BTS (Base Transreceiver Station)
BTS is the equipment used for transmitting and receiving radio signals between MS and a network. BTS’s create cell structure. Mobile devices under the cell can communicate with the rest of the network. BTS’s are connected to BSC’s which controls them.
BSC (Base Station Controller)
BSC is the intelligence behind the BTS’s. It can control multiple BTS’s. BSC is responsible for allocation of radio frequencies, power and signal measurements. BSC also controls handover between one cell to another if they are under the control of same BSC. (Inter BTS, Intra BSC handover). Or BSC can change the mobile device’s frequency under the same BTS in case the transmission at a certain frequency is impossible because of some circumstances. This is called Intra BTS handover.
MSC (Mobile Switching Center)
MSC is the core element of the Network Switching Subsystem (NSS). It is responsible for routing voice calls and SMS. MSC sets up end-to-end circuit switched connection between subscribers. It handles mobile services such as registration, authentication, location updating and Inter BSC-Intra MSC handovers.
GMSC (Gateway MSC)
GMSC is a special kind of MSC that is used to route calls outside the mobile network. Whenever a call for a mobile subscriber comes from outside the mobile network (PSTN), or the subscriber wants to make a call to somebody outside the mobile network the call is routed through the GMSC.
HLR (Home Location Register)
HLR is the main and the most important database of a carrier. It stores all the data related to the subscriber such as GSM services that the subscriber is using, current location of a subscriber etc. HLR contains details of each SIM card issued by the carrier. IMSI and MSISDN are the primary keys. Data stored HLR is permanent.
VLR (Visitor Location Register)
VLR is a database like HLR but it is not permanent. It stores temporary information of subscriber that may be needed by MSC. VLR is always integrated with MSC. When an MS (Mobile Station) appears in a new MSC area, the VLR connected to that MSC will request the subscriber data from the HLR. When the MS wants to place a call, MSC will query VLR first instead of HLR. So VLR decreases the number of queries sent to HLR.
EIR (Equipment Identity Register)
EIR is a database that stores list of mobile stations (MS) which are allowed to use the network or banned from network. This allows tracking of lost or stolen devices. Mobile Stations are identified by their IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity).
AuC (Authentication Center)
AuC is a function used to authenticate a mobile subscriber that attempts to connect to the GSM network. Authentication is done by identification and verification of the validity of the SIM card.
When a subscriber authenticates, AuC generates parameters used for the privacy and encryption. To ensure privacy, TMSI (Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity) is assigned to a subscriber for the duration that the subscriber remains under control of the MSC associated with the AuC. TMSI is used instead of IMSI. Because TMSI is randomly generated while IMSI is unique. Thus, identity of the subscriber is protected.